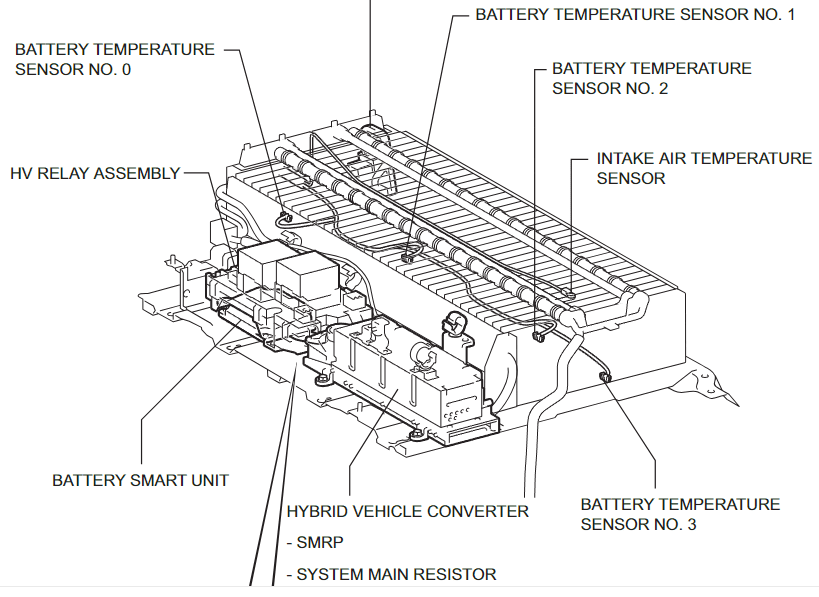
Toyota hybrid battery type
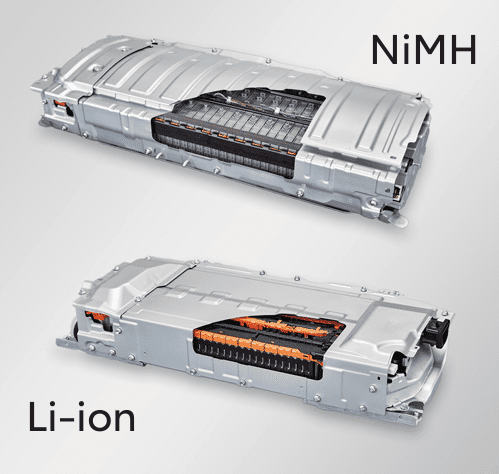

Toyota’s hybrid battery technology encompasses both Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) and Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) batteries, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Below is an overview of their specifications, safety features, reliability, and future developments:
🔋 Toyota hybrid battery type & Specifications
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH):
- Usage: Predominantly in earlier hybrid models.
- Voltage: Typically around 201.6V.
- Capacity: Approximately 6.5Ah.
- Weight: Around 1.04kg per module.
- Dimensions: Approximately 19.6mm (W) × 106mm (H) × 285mm (L).
- Cooling: Primarily air-cooled systems.
- Advantages: Proven reliability, cost-effective, and robust performance.(hybrids.co.nz)
Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion):
- Usage: Common in newer hybrid and plug-in hybrid models.
- Voltage: Ranges from 207V to 355V, depending on the model.
- Capacity: Varies between 1.0 kWh to 18.1 kWh.
- Cooling: Employs both air and liquid cooling systems.
- Advantages: Higher energy density, lighter weight, and improved efficiency.
For a comprehensive comparison between NiMH and Li-Ion batteries in hybrid electric vehicles, you can refer to this detailed analysis: (a3global.com).
🛡️ Safety Characteristics
Toyota prioritizes safety in its hybrid battery systems through several measures:
- Sealed Battery Packs: All high-voltage circuits are sealed and protected from casual contact, minimizing the risk of electric shock.
- Color-Coded High-Voltage Components: High-voltage circuits are clearly marked and color-coded for easy identification.
- Automatic Shutdown: In the event of a collision, the system automatically disconnects the high-voltage battery to prevent potential hazards.
- Thermal Management: Advanced cooling systems prevent overheating, ensuring optimal battery performance and longevity.(support.toyota.com)
For more detailed information on safety features, visit Toyota’s official safety guidelines: (support.toyota.com).
🔧 Reliability & Longevity
Toyota’s hybrid batteries are renowned for their durability:
- Lifespan: Typically last between 8 to 15 years or 100,000 to 200,000 miles, depending on usage and maintenance.
- Warranty: Since 2020, Toyota offers a 10-year or 150,000-mile warranty on hybrid batteries, with annual health checks extending coverage up to 15 years.
- Maintenance: Minimal maintenance required, with many batteries lasting the vehicle’s lifetime.(thehybridgeek.com, Reddit)
For insights from Toyota hybrid owners on battery longevity and replacement costs, consider reading this article: (Torque News).
🔮 Future Developments
Toyota is actively investing in next-generation battery technologies:
- Solid-State Batteries: These promise higher energy density, faster charging times, and enhanced safety. Toyota aims to commence mass production by 2027-2028.
- Recycling Initiatives: Collaborations with companies like Redwood Materials focus on recycling old hybrid batteries to produce new ones, promoting sustainability.
- Hybrid Expansion: In response to market trends, Toyota is increasing its hybrid offerings, with hybrids accounting for 37% of sales by mid-2024.(Toyota EU, axios.com, reuters.com)
For more on Toyota’s battery technology roadmap, visit: (Toyota EU).
🖼️ Visual Resources – Toyota hybrid battery type
To better understand Toyota’s hybrid battery systems, here are some visual resources:
- Toyota Hybrid Battery Overview: An in-depth look at the components and functioning of Toyota’s hybrid batteries.
- NiMH vs. Li-Ion Batteries: A comparative analysis highlighting the differences between the two battery types.
- Solid-State Battery Technology: Insights into Toyota’s upcoming solid-state battery advancements.(toyotaclevelandheights.com)
Note: As a text-based AI developed by OpenAI, I cannot display images directly. However, you can find these visuals by searching the titles above online.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) and Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion)
Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) vs. Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries in Toyota Cars
| Feature | Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) | Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Older Toyota hybrids (e.g., Prius, Camry Hybrid) | Newer Toyota hybrids and plug-in hybrids (e.g., RAV4) |
| Energy Density | Lower (40-60 Wh/kg) | Higher (100-265 Wh/kg) |
| Weight | Heavier due to lower energy density | Lighter, higher energy per kg |
| Charge/Discharge Rate | Moderate, suited for steady hybrid use | Faster, ideal for EVs and high-performance hybrids |
| Thermal Management | Air-cooled (simple, reliable) | Air-cooled or liquid-cooled (better thermal control) |
| Cost | Generally cheaper to manufacture | More expensive due to advanced materials |
| Lifespan | 8-15 years (good thermal stability) | 8-12 years (dependent on usage and cooling) |
| Safety | Stable, less prone to thermal runaway | Requires sophisticated BMS for safety |
| Environmental Impact | Less efficient recycling but less toxic | More recyclable but contains more hazardous materials |
| Charging Efficiency | Lower, with more energy loss during charge | Higher efficiency, faster charging |
| Application | Preferred in budget hybrids (Yaris Hybrid) | Used in performance and plug-in hybrids (RAV4 Prime) |
Why Toyota Uses Both:
- NiMH: Used in budget-friendly hybrids for cost-effectiveness and long life.
- Li-Ion: Used in premium hybrids and plug-in hybrids for superior performance, lighter weight, and faster charging.
List of current Toyota hybrid models and the type of battery they use:
Toyota Models Using NiMH Batteries:
- Toyota Prius (Base Models)
- Toyota Corolla Hybrid (Some Markets)
- Toyota Camry Hybrid (Base Models)
- Toyota Highlander Hybrid (Some Versions)
- Toyota Yaris Hybrid (Some Versions)
- Toyota Sienna Hybrid (Some Versions)
Toyota Models Using Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) Batteries:
- Toyota Prius (High-End Trims and Plug-in Hybrid – Prius Prime)
- Toyota Corolla Cross Hybrid
- Toyota RAV4 Hybrid (Some Versions)
- Toyota RAV4 Prime (Plug-in Hybrid)
- Toyota Camry Hybrid (Higher Trims)
- Toyota Highlander Hybrid (Higher Trims)
- Toyota Venza Hybrid
- Toyota Mirai (Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle – Uses Li-Ion for hybrid drive)
- Toyota Yaris Cross Hybrid
- Toyota C-HR Hybrid
Toyota Hybrid Battery Specifications (2024)
| Model | Battery Type | Capacity | Voltage | Cooling Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota Prius | NiMH/Li-Ion | 1.3-13.6 kWh | 201.6-355V | Air/Liquid-Cooled |
| Toyota Corolla Hybrid | NiMH/Li-Ion | 1.3-4.4 kWh | 201.6-259V | Air-Cooled |
| Toyota Corolla Cross | Li-Ion | 1.08 kWh | 259V | Air-Cooled |
| Toyota Camry Hybrid | NiMH/Li-Ion | 1.0-1.6 kWh | 245V | Air-Cooled |
| Toyota RAV4 Hybrid | Li-Ion | 1.6 kWh | 259V | Liquid-Cooled |
| Toyota RAV4 Prime | Li-Ion | 18.1 kWh | 355V | Liquid-Cooled |
| Toyota Highlander | NiMH/Li-Ion | 1.9 kWh | 288V | Air/Liquid-Cooled |
| Toyota Venza Hybrid | Li-Ion | 1.0 kWh | 259V | Air-Cooled |
| Toyota Sienna Hybrid | NiMH | 1.9 kWh | 288V | Air-Cooled |
| Toyota Mirai | Li-Ion | 1.24 kWh | 310.8V | Air-Cooled |
| Toyota Yaris Hybrid | NiMH/Li-Ion | 0.76-4.3 kWh | 177.6-207.2V | Air-Cooled |
| Toyota C-HR Hybrid | Li-Ion | 1.08 kWh | 259V | Air-Cooled |