Toyota Tundra engine problems
The Toyota Tundra is a well-regarded full-size pickup truck known for its durability and performance, but like all vehicles, it has had some engine-related issues reported by owners, particularly in certain model years or engine types. Here are the most common Toyota Tundra engine issues, along with potential causes and solutions:
1. Air Injection Pump Failure
- Affected Models: Primarily Tundras with the 5.7L V8 engine (2007–2013).
- Symptoms:
- Check engine light (CEL) illuminated.
- The truck may go into “limp mode”, reducing engine power.
- Whining noise from the engine bay.
- Cause: The air injection pump, responsible for reducing emissions during cold starts, tends to fail due to moisture and debris entering the system.
- Solution:
- Replace the air injection pump and related components (valves and sensors).
- Some owners install aftermarket kits to bypass the air injection pump and avoid costly repairs.
2. Secondary Air Injection System Issues
- Affected Models: 2007–2013 Tundras, especially with the 5.7L engine.
- Symptoms:
- CEL on.
- Engine power is reduced.
- The vehicle may go into limp mode, reducing performance.
- Cause: The air injection system, designed to help reduce emissions on cold starts, can become clogged with carbon or fail due to faulty valves or the air pump.
- Solution:
- Replace the faulty air pump and valves.
- Some owners install a bypass module to avoid recurring issues.
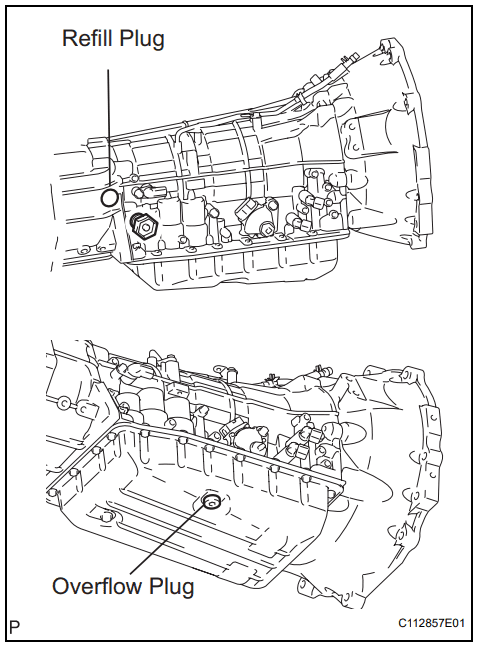
3. Camshaft Tower Leak
- Affected Models: Primarily 5.7L V8 engines (2007-2011).
- Symptoms:
- Oil leaks around the engine block, especially near the camshaft tower.
- Noticeable oil stains on the ground or engine bay.
- Cause: A common problem on early 5.7L V8 engines, where the camshaft towers (where the camshaft is mounted) are prone to leaking oil.
- Solution:
- Toyota issued a Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) for this issue, and it can be repaired under warranty if applicable.
- The repair involves resealing the camshaft tower with proper gasket material.
4. Timing Chain Tensioner Failure
- Affected Models: 5.7L V8 and 4.6L V8 engines (mostly older models).
- Symptoms:
- Rattling or ticking noise from the engine, especially on cold starts.
- CEL on in some cases.
- Cause: The timing chain tensioner can wear out over time, causing improper tension on the timing chain, leading to noise and potentially severe engine damage.
- Solution:
- Replace the timing chain tensioner, and inspect the timing chain for wear.
- If the timing chain is stretched, it may need replacement as well.
5. Excessive Oil Consumption
- Affected Models: Some older Toyota Tundra models with the 4.7L V8 engine.
- Symptoms:
- Engine oil levels drop rapidly between oil changes.
- Blue smoke from the exhaust during acceleration.
- Cause: Worn piston rings, valve seals, or other internal engine components can allow oil to burn in the combustion chamber.
- Solution:
- Conduct a compression test to confirm internal engine wear.
- Rebuild or replace worn piston rings, valve seals, or other components causing the issue.
- In severe cases, the engine may need to be replaced or rebuilt.
6. Head Gasket Failure
- Affected Models: Some Tundras with high mileage, particularly those equipped with the 4.7L V8 engine.
- Symptoms:
- Overheating.
- Coolant loss with no visible leaks.
- White smoke from the exhaust (indicating coolant burning in the combustion chamber).
- Milky oil (a mixture of oil and coolant).
- Cause: Over time, the head gasket can fail due to overheating, poor maintenance, or natural wear, allowing coolant to leak into the engine.
- Solution:
- Replace the head gasket and inspect the cylinder head for warping or cracks.
- If the cylinder head is damaged, it may need to be machined or replaced.
7. Radiator and Cooling System Issues
- Affected Models: Primarily older models or those with high mileage.
- Symptoms:
- Engine overheating.
- Coolant leaks or loss of coolant.
- Radiator hoses becoming brittle or bursting.
- Cause: Over time, radiators can become clogged with debris or corrode, reducing their ability to cool the engine. In addition, radiator hoses can weaken and leak.
- Solution:
- Replace the radiator and hoses if necessary.
- Regular coolant flushes can prevent debris buildup and corrosion.
- Check and replace the radiator cap if it’s not maintaining proper pressure.
8. Throttle Body Issues
- Affected Models: Older Toyota Tundras, particularly the first generation (2000-2006).
- Symptoms:
- Erratic idle.
- CEL on.
- Reduced engine performance or stalling.
- Cause: Carbon buildup in the throttle body can cause improper airflow, leading to rough idling or stalling.
- Solution:
- Clean the throttle body with a throttle body cleaner to remove carbon buildup.
- If the issue persists, the throttle body may need to be replaced.
9. Fuel Injector Problems
- Affected Models: Common in high-mileage Tundras, especially those using lower-quality fuel.
- Symptoms:
- Poor fuel economy.
- Rough idle or misfires.
- CEL illuminated.
- Cause: Clogged or faulty fuel injectors can cause improper fuel delivery to the engine, leading to misfires and poor performance.
- Solution:
- Clean the fuel injectors using a fuel system cleaner.
- If cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue, replace the faulty injectors.
10. Catalytic Converter Failure
- Affected Models: Older Tundras, especially those that have experienced engine issues like excessive oil consumption or misfires.
- Symptoms:
- CEL illuminated with codes related to emissions (P0420/P0430).
- Loss of power or poor acceleration.
- Increased emissions.
- Cause: The catalytic converter can become clogged or fail, especially if the engine burns oil or has misfiring issues, causing unburned fuel to enter the exhaust system.
- Solution:
- Replace the catalytic converter.
- Address any underlying engine issues (e.g., misfires or oil burning) to prevent future failure.
Preventive Maintenance Tips for Toyota Tundra Engines
- Regular Oil Changes: Follow the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals (every 5,000 to 10,000 miles, depending on driving conditions). Using high-quality synthetic oil can help prolong engine life.
- Coolant System Maintenance: Flush the cooling system and replace coolant every 50,000 to 100,000 miles to prevent overheating and corrosion in the radiator and water pump.
- Replace Spark Plugs: Change spark plugs at the recommended intervals (usually every 100,000 miles) to prevent misfires and maintain optimal fuel efficiency.
- Inspect Belts and Hoses: Regularly inspect and replace worn serpentine belts, radiator hoses, and other key components that can fail over time.
- Throttle Body Cleaning: Clean the throttle body periodically to prevent buildup that can lead to idle issues.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Use high-quality gasoline and consider using a fuel injector cleaner to keep the injectors functioning properly.
By staying on top of regular maintenance and addressing issues early, you can avoid more serious problems with your Toyota Tundra’s engine.