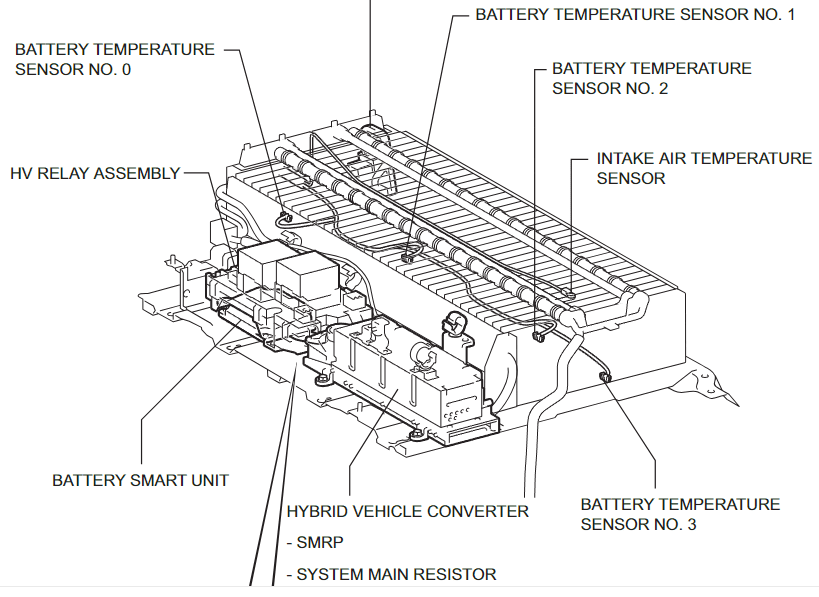
Toyota hybrid battery degradation
Here’s a comprehensive explanation of Toyota hybrid battery degradation — its causes, symptoms, prevention, and solutions —
🔋 Toyota Hybrid Battery Degradation: What You Should Know
Toyota has long been a pioneer in hybrid technology, with models like the Toyota Prius, Camry Hybrid, RAV4 Hybrid, and Highlander Hybrid earning reputations for fuel efficiency and longevity. At the heart of these vehicles is the hybrid battery pack, which works alongside a gasoline engine to deliver improved mileage and lower emissions.
While Toyota hybrid batteries are engineered to last — often over 150,000 miles or more — battery degradation is a reality that can affect performance, efficiency, and driving experience over time.
🔧 What Is Hybrid Battery Degradation?
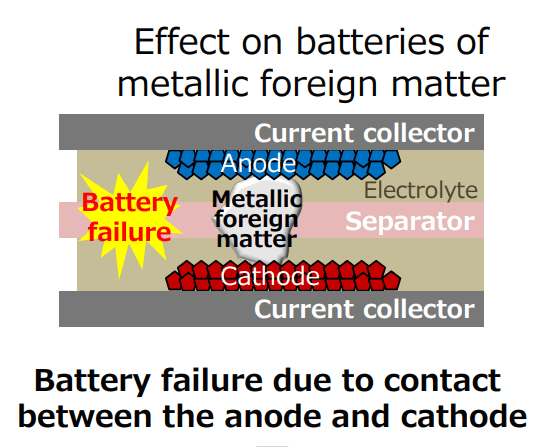
Battery degradation refers to the gradual loss of a battery’s ability to hold and deliver charge. In hybrids, the high-voltage battery pack is typically made of Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) or Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) cells. Over time and use, the chemical composition inside these cells changes, leading to a reduction in performance and capacity.
Degradation doesn’t mean the battery instantly fails — rather, it becomes less efficient, which may affect fuel economy and acceleration.
📉 Causes of Toyota Hybrid Battery Degradation
- Age and Usage
- Just like any rechargeable battery, the cells degrade over time with repeated charge-discharge cycles.
- The typical lifespan is around 8–15 years, depending on driving habits and environment.
- High Temperatures
- Heat is the enemy of batteries. Prolonged exposure to hot climates can speed up degradation.
- Inadequate ventilation or a clogged battery cooling fan exacerbates the problem.
- Short Trips or Irregular Use
- Consistently short trips don’t allow the battery to complete full charging cycles, which may lead to imbalance among cells.
- Long periods of inactivity may also accelerate deterioration.
- Poor Maintenance
- Ignoring the hybrid system’s health, not cleaning the battery fan, or failing to monitor warning signs can accelerate wear.
- Manufacturing Variation
- Some individual battery modules may degrade faster than others due to small differences in internal resistance or manufacturing inconsistencies.
⚠️ Symptoms of a Degrading Hybrid Battery
While Toyota’s onboard diagnostics will often detect major battery issues, here are some common symptoms of gradual degradation:
- Noticeably Reduced Fuel Economy
- Frequent Engine Kick-Ins: The gas engine runs more often, as the battery can’t contribute as much.
- Battery Charge Fluctuations: Rapid changes in battery level on the display, from full to low or vice versa.
- Decreased Acceleration Performance
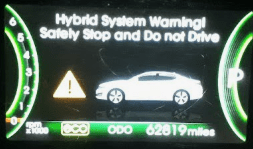
- Warning Lights: The “Check Hybrid System” message or battery warning light may appear.
- Unusual Noises from the Rear Seat Area (in vehicles where the battery fan is located) — indicating the cooling fan is working harder.
🛡️ How Toyota Designs Minimize Degradation
Toyota hybrids include battery management systems (BMS) that help extend battery life:
- Charge Range Limits: Batteries are never fully charged or fully depleted. Typically, the system operates between 40%–80% of actual capacity, which significantly reduces wear.
- Thermal Management: Hybrid batteries are cooled with air (and in newer models, with liquid). The BMS adjusts fan speed or coolant flow based on temperature.
- Cell Balancing: The control system continuously balances voltage across all battery modules.
These technologies help Toyota batteries outlast those in many competitors.
🛠️ Maintenance and Prevention Tips
- Keep the Battery Fan Clean
- In models like the Prius or Camry Hybrid, the fan draws air from inside the cabin. Dust, pet hair, and debris can clog the intake.
- Cleaning every 30,000–50,000 miles is recommended.
- Avoid Extreme Heat
- Park in the shade or a garage when possible.
- Use your car’s AC wisely to help maintain a stable internal temperature.
- Drive Regularly
- Hybrid batteries prefer regular use. Letting the vehicle sit for weeks or months may cause cells to drift or weaken.
- Don’t Ignore Warning Lights
- Have the hybrid system scanned for codes if a warning light appears.
- A diagnostic tool like Techstream can read specific battery voltages and internal resistance of each module.
- Battery Reconditioning
- This process balances and restores the capacity of battery modules.
- Available through some Toyota dealerships and hybrid specialists, it can prolong battery life without a full replacement.
🔁 Repair and Replacement Options
If degradation becomes severe, you have several options:
| Option | Description | Cost Estimate (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| New OEM Battery | Brand-new battery from Toyota | $2,000 – $3,500 |
| Reconditioned Battery | Refurbished with replaced weak modules | $900 – $1,500 |
| Module Replacement | Replace only the bad cells | $500 – $1,000 (temporary fix) |
Note: Newer hybrids like the RAV4 Prime and Prius Prime often use Li-ion packs which degrade differently — they’re lighter and denser but may have shorter lifespans in hot climates.
✅ Conclusion
While Toyota hybrid batteries do degrade over time, proper maintenance, driving habits, and early intervention can significantly extend their lifespan. In fact, many Toyota hybrids are still on the road with their original batteries well beyond 200,000 miles.
Toyota’s robust engineering, smart battery management systems, and widespread service network make hybrid ownership a reliable and cost-effective choice, even as the battery ages. Staying proactive can ensure you get the best performance and value out of your hybrid vehicle.
Would you like a checklist for battery health monitoring, or help choosing between a new vs. reconditioned battery?
Toyota hybrid battery PDF
Toyota hybrid batteries are renowned for their durability, often lasting well over 150,000 miles. However, like all batteries, they can degrade over time.
📚 Additional Resources
- GreenCars: EV Battery Degradation and Prevention
- Toyota Support: Hybrid Battery Maintenance
- Kelley Blue Book: Hybrid Battery Health Tips
- Toyota of Bellevue: Hybrid Battery Maintenance
—