Toyota Engines
Toyota engines are recognized globally for their reliability, durability, and advanced engineering. Over the decades, Toyota has developed a wide range of engines—from fuel-efficient inline-4s to powerful V6s and V8s, hybrid powertrains, and the latest battery-electric and hydrogen systems. In this in-depth overview, we’ll explore Toyota’s engine evolution, major engine families, innovations, and current direction in more than 600 words, with helpful links and pictures.
🔧 1. A Legacy of Innovation
Toyota’s engine development history began in the 1930s, with mass production starting in the post-World War II era. Early engines like the Toyota Type A (1935) were simple, yet they laid the foundation for robust engine development. Fast forward to the 21st century, and Toyota now leads in hybrid technology, turbocharging efficiency, and low-emission engines.
🚗 2. Major Toyota Engine Families
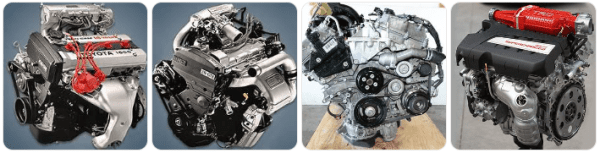
a. A-Series Engines (e.g., 4A GE)
🔧 Toyota 4A GE Engine
The 4A GE is a renowned 1.6-liter inline-four engine, celebrated for its performance and reliability. It was prominently featured in models like the AE86 Corolla Levin and Sprinter Trueno. Notable for its high-revving nature and twin-cam design, it became a favorite among enthusiasts and racers.
- Legendary for their reliability and performance, especially the 4A GE 1.6L DOHC 16-valve engine that powered cars like the AE86.
- Nicknamed “The Screamer” due to its high-revving nature.
b. S-Series Engines (e.g., 3S GTE)
🔧 Toyota 3S GTE Engine
The 3S GTE is a 2.0-liter turbocharged inline-four engine, known for its robust performance. It powered vehicles like the Toyota Celica GT-Four and MR2 Turbo. With its cast-iron block and aluminum head, it offered a balance of strength and weight, making it a popular choice for performance applications
- Known for turbocharged performance.
- The 3S GTE was used in the Toyota Celica GT-Four and MR2 Turbo.
- Strong aftermarket support and tuning potential.
c. GR Family (e.g., 2GR FE, 3.5L V6)
🔧 Toyota 2GR FE Engine
The 2GR FE is a 3.5-liter V6 engine, part of Toyota’s GR family. It’s widely used across various Toyota and Lexus models, including the Camry, Highlander, and RX series. Known for its smooth power delivery and efficiency, it features technologies like Dual VVT-i to optimize performance.
- One of Toyota’s most widely used V6 engines.
- Found in the Camry, Highlander, Sienna, Lexus RX, and Lotus Evora.
- Known for smooth power delivery and long-term durability.
d. Dynamic Force Engines (New TNGA-Based)
- Launched with Toyota’s TNGA (Toyota New Global Architecture) in 2017.
- Engines like the M20A-FKS and A25A-FKS have:
- High thermal efficiency (~40%)
- Direct & port fuel injection (D-4S)
- Atkinson Cycle compatibility for hybrids
🔗 Toyota Dynamic Force Engine Details
🌱 3. Hybrid Powertrains
Toyota revolutionized the automotive world with the Toyota Prius in 1997—the first mass-produced hybrid. Since then, Toyota’s Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD) has powered millions of vehicles.
- Key Components:
- Internal combustion engine (ICE)
- Electric motor(s)
- Power split device (planetary gearset)
- Battery pack (NiMH or Li-ion)
🔗 Toyota Hybrid System Explained
⚡ 4. Electric and Hydrogen Powertrains
a. BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles)
Toyota is expanding its bZ (Beyond Zero) lineup, starting with the bZ4X. While not using traditional engines, these vehicles use electric motors powered by lithium-ion batteries.
b. Hydrogen Fuel Cell – Toyota Mirai
Instead of a conventional engine, the Toyota Mirai uses a hydrogen fuel cell stack to generate electricity. It emits only water vapor.
- Fuel cell = Clean power generation
- Range: ~400–500 km per tank
🧠 5. Engine Technology Innovations
a. D-4S Fuel Injection
- Toyota combines direct and port fuel injection in a single engine, optimizing performance and emissions.
b. Variable Valve Timing (VVT-i, VVT-iE)
- Adjusts timing of valve opening to improve efficiency and torque at different RPMs.
c. Atkinson Cycle
- Used in hybrids for better fuel economy, sacrificing some power for thermal efficiency.
🧪 6. Engine Testing and Quality
Toyota is renowned for its stringent quality control. Every engine goes through extensive durability testing—some clock over 1 million km in lab conditions. This is part of what gives Toyota engines their long lifespan.
⚠️ 7. Known Issues in Some Engines
- Oil consumption: Found in some older 2AZ-FE 2.4L engines.
- Carbon build-up: In some D-4 direct-injection engines without port cleaning.
- Head gasket issues: Rare, but known in early 3.0L V6s (1MZ-FE) due to overheating.
However, Toyota addressed most of these issues in later generations with improved materials and engineering.
✅ Conclusion
Toyota engines represent a harmonious blend of durability, performance, and cutting-edge efficiency. From the iconic 4A-GE and turbocharged 3S-GTE, to the modern 2GR-FE and Dynamic Force engines, Toyota continues to evolve. Now venturing into electrification, hydrogen, and software-based systems, the “engine” at Toyota is not just mechanical—it’s also electric and intelligent.
📘 Helpful Links Summary
- 🔗 Toyota Global Engine Technology Overview
- 🔗 Toyota Hybrid Technology
- 🔗 Toyota Technical Manuals & PDFs
- 🔗 Woven by Toyota (Future Mobility)
- 🔗 Toyota bZ Series (BEVs)