Toyota electronic throttle control system problem
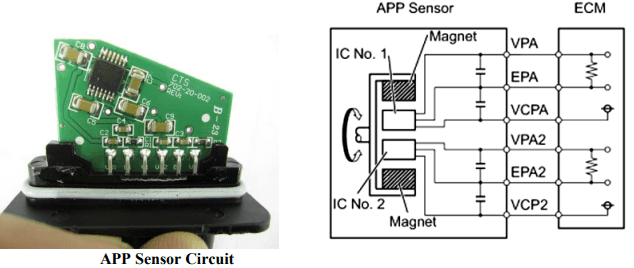
Toyota electronic throttle control system problem
ETCS (Toyota electronic throttle control system) problem
Toyota’s Electronic Throttle Control System (ETCS) gained attention due to unintended acceleration incidents in the early 2010s, which led to recalls, lawsuits, and significant media coverage. The issue mainly affected Toyota models produced in the mid-2000s and was one of the company’s most significant safety-related challenges.
Here’s a breakdown of the ETCS issues and Toyota’s response:
Nature of the Problem:
The ETCS in Toyota vehicles replaced traditional mechanical linkage between the accelerator pedal and the throttle with an electronic signal. The system was intended to offer smoother and more precise throttle control. However, some drivers reported incidents where the vehicle would unexpectedly accelerate without pressing the gas pedal.
Possible Causes:
- Sticking Accelerator Pedals: Some cases were traced to accelerator pedals that could stick, which was often due to wear and environmental factors like moisture and temperature.
- Floor Mat Interference: Poorly fitted floor mats, especially non-original ones, were identified as a cause, as they could slide forward and press against the accelerator pedal.
- Software and Electrical Concerns: There were suspicions about software bugs or electrical interference in the ETCS that might contribute to unintended acceleration. However, Toyota has consistently maintained that there were no electronic flaws in the system. In 2011, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and NASA conducted an investigation, concluding that software issues were not a cause of unintended acceleration in Toyota vehicles.
Toyota’s Response:
- Massive Recalls: Toyota issued recalls to address these problems, focusing on modifying or replacing accelerator pedals, installing brake override systems (which cut throttle input if the brakes are applied), and securing or modifying floor mats.
- Brake Override System: Toyota implemented a brake override system in vehicles to prevent unintended acceleration by prioritizing brake inputs over throttle inputs.
- Safety Improvements in ETCS: Since the recall, Toyota has continuously improved its ETCS to ensure that such issues do not recur, adding redundancies and further safety checks to the system.
Impact on Toyota’s Reputation:
While the unintended acceleration issue led to fines and settlements, Toyota’s transparent and large-scale recall response helped to reassure consumers over time. Since these incidents, Toyota has enhanced its focus on safety and quality control, incorporating more robust testing for new electronic components and software.
Since these recalls and updates, no major issues with the ETCS have been reported in recent Toyota models.

My 2014 Camry while hitting the resume button just took off almost wide open. Finally got it to shut off. My son had 2017 Tacoma that did the exact thing when it was just a month old with very low miles. Deal ship found nothing wrong. We never used the cruise on the Tacoma again. I guess I won’t use the cruise on my Camry. Nothing bad happen either time but it could have. I am going to have it checked my a mechanic.
If you’re experiencing issues with the cruise control system in your 2014 Toyota Camry, several factors could be contributing to the problem. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you diagnose and potentially resolve the issue:
https://toyotaspace.com/2014-camry-cruise-control-not-working/