Toyota Camry Cooling System 2AZ FE Engine
Troubleshooting and maintaining the cooling system in a Toyota Camry equipped with the 2AZ-FE engine is essential to prevent overheating and ensure long engine life. Issues in the cooling system can range from leaks to thermostat or radiator problems. Here’s a guide on how to troubleshoot and maintain the cooling system for this specific engine.
1. Common Cooling System Issues in the 2AZ FE Engine
- Coolant Leaks: Often caused by worn gaskets, radiator, water pump, or hoses.
- Overheating: Due to a faulty thermostat, clogged radiator, malfunctioning water pump, or low coolant levels.
- Heater Not Working: Often related to low coolant, air trapped in the system, or a malfunctioning heater core.
- Coolant Loss: Internal coolant leaks can be due to head gasket failure, while external leaks are usually visible around hoses, the radiator, or the water pump.
- Radiator Fan Failure: Can cause overheating, especially in slow traffic, due to electrical or fan motor issues.
2. Troubleshooting Steps for Cooling System Issues
a. Inspect for Coolant Leaks
- Visual Inspection:
- Check under the car for coolant puddles or stains.
- Inspect radiator hoses, the radiator, and around the water pump for signs of leaks.
- Check around the cylinder head gasket for any signs of coolant mixing with engine oil (milky oil) or white exhaust smoke (indicative of a blown head gasket).
b. Check Coolant Levels
- Ensure the coolant level in both the radiator and the overflow reservoir is correct. Low coolant levels can cause overheating.
- Coolant Type: Use the correct Toyota Super Long Life coolant (pink or red) for best performance and to avoid corrosion.
c. Test the Thermostat
- The thermostat regulates engine temperature by controlling coolant flow. If stuck closed, it can cause overheating; if stuck open, the engine might run too cool.
- Test: After starting the engine, let it warm up. Feel the upper radiator hose:
- If it stays cold even when the engine is hot, the thermostat may be stuck closed.
- If it feels warm but the engine still overheats, it might be partially stuck open or blocked.
d. Inspect the Radiator and Radiator Cap – 2AZ Fe Engine Radiator –
- Radiator Blockage: Check for debris or corrosion on the radiator fins, which could impede airflow.
- Coolant Flow: A clogged radiator can prevent proper coolant circulation. You can flush the radiator or have it tested by a mechanic.
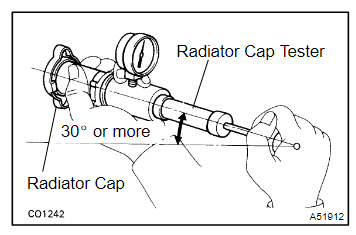
- Radiator Cap: A weak or faulty cap may not hold pressure, which could cause coolant to boil over. Replace it if it shows signs of wear.
e. Check the Water Pump
- The water pump circulates coolant through the engine. A faulty water pump can cause overheating.
- Symptoms of a Bad Water Pump:
- Coolant leaks around the pump.
- Squealing or grinding noises coming from the pump area.
- Overheating due to poor coolant circulation.
f. Radiator Fan Functionality
- The radiator fan helps keep the engine cool, especially when idling or driving slowly.
- Check if the fan turns on when the engine heats up.
- If the fan doesn’t run, it could be due to a blown fuse, bad fan motor, or faulty temperature sensor.
g. Test for Air in the System
- Air pockets in the cooling system can cause erratic temperature readings and poor heating performance.
- Bleed the system to remove trapped air:
- Open the radiator cap (when the engine is cold).
- Start the engine and let it run, topping off the coolant as air bubbles are purged.
h. Check the Heater Core
- If your heater isn’t blowing warm air, it could be due to a clogged heater core or low coolant levels.
- Inspect the heater hoses. If one is hot and the other is cold, the core might be blocked and need flushing or replacement.
i. Head Gasket Issues
- Symptoms of a blown head gasket:
- White smoke from the exhaust.
- Coolant mixing with engine oil (resulting in milky oil).
- Overheating, especially when driving at high speeds or under load.
- Coolant loss without visible external leaks.
- A compression test or a combustion leak test can confirm if the head gasket is failing.
3. Maintenance Tips for the Toyota 2AZ FE Cooling System
a. Regular Coolant Flushes
- Over time, coolant can degrade and become contaminated. It’s important to replace it at recommended intervals (every 30,000 miles or 5 years, depending on coolant type).
- Procedure:
- Drain the old coolant from the radiator.
- Flush the system with distilled water.
- Refill with fresh Toyota Super Long Life coolant.
b. Radiator Maintenance
- Inspect the radiator regularly for signs of corrosion or blockage. Clean the fins of any debris.
- Ensure the radiator cap is functioning properly to maintain proper system pressure.
c. Check Hoses and Belts
- Radiator hoses should be inspected for cracks, bulges, or leaks. Replace any worn or cracked hoses.
- Check the serpentine belt that drives the water pump for wear or damage. If the belt is loose or worn, it can affect coolant circulation.
d. Test the Thermostat Periodically
- Even if no issues are present, it’s a good idea to replace the thermostat during a major coolant system service. This prevents it from failing unexpectedly.
e. Water Pump Inspection
- During a timing belt or chain service, inspect the water pump and replace it if there are signs of wear or leakage.
f. Keep the Radiator Fan Operational
- The fan motor or relay can wear out over time, especially in older vehicles. Regularly check that the fan comes on as the engine warms up. Replace any faulty components as needed.
4. Special Considerations for the 2AZ FE Engine
- Head Gasket Issues: The 2AZ-FE engine is prone to head gasket problems, which can affect the cooling system. If the engine overheats due to coolant loss or a head gasket issue, address it quickly to avoid further engine damage.
- Coolant Type: Always use Toyota-recommended coolant (Super Long Life Coolant), which is designed to prevent corrosion and maintain proper temperature regulation.
Conclusion
Maintaining the cooling system in your Toyota Camry with the 2AZ-FE engine is crucial for preventing overheating and long-term engine damage. Regularly check coolant levels, inspect for leaks, and replace key components like the thermostat, radiator, and water pump as needed. If you encounter persistent issues, a thorough inspection of the head gasket may be necessary, given this engine’s known susceptibility to head gasket failure.