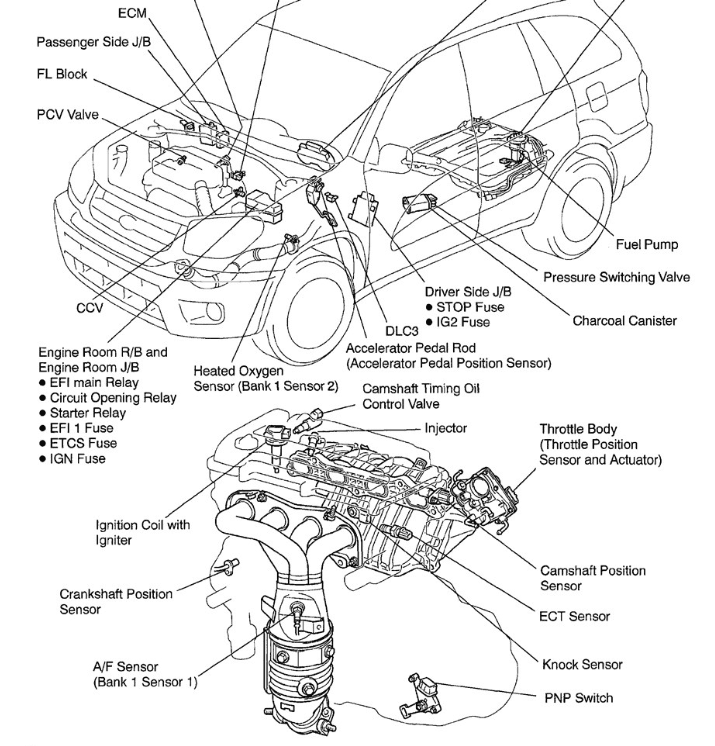
RAV4 brake system
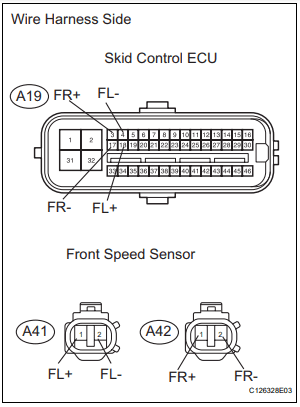
- DTC C0200/31 Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Signal
- DTC C0205/32 Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Signal
- DTC C1235/35 Foreign Object is Attached on Tip of Front Speed Sensor RH
- DTC C1236/36 Foreign Object is Attached on Tip of Front Speed Sensor LH
- DTC C1271/71 Low Output Signal of Front Speed Sensor RH (Test Mode DTC)
- DTC C1272/72 Low Output Signal of Front Speed Sensor LH (Test Mode DTC)
- DTC C1275/75 Abnormal Change in Output Signal of Front Speed Sensor RH (Test Mode DTC)
- DTC C1276/76 Abnormal Change in Output Signal of Front Speed Sensor LH (Test Mode DTC)
VEHICLE STABILITY CONTROL SYSTEM PDF – RAV4 brake system
The brake system of a Toyota RAV4 typically includes the following components and features:
Key Components:
- Brake Pedal and Master Cylinder:
- The brake pedal is connected to the master cylinder, which converts pedal pressure into hydraulic pressure.
- Dual circuit hydraulic systems are common for redundancy.
- Brake Booster:
- Enhances the force applied by the driver, reducing the effort needed to operate the brakes.
- Disc Brakes:
- Front and rear wheels typically have disc brakes for efficient stopping power.
- Ventilated rotors are often used on the front for better cooling.
- Brake Pads:
- Friction materials pressed against the rotors to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS):
- Prevents wheel lock-up during emergency braking, maintaining steering control.
- Sensors monitor wheel speed to modulate brake force as needed.
- Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD):
- Balances braking force between front and rear wheels, improving stability.
- Brake Lines and Hoses:
- Transfer hydraulic fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers.
- Parking Brake:
- Usually electronically controlled in newer RAV4 models, engaging the rear brakes when activated.
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Traction Control:
- These systems may integrate with the brakes to prevent skidding and loss of traction.
Types of Brakes:
- Disc Brakes: Used on both front and rear wheels.
- Drum Brakes (older models): Sometimes found on rear wheels in older models or base trims.
Maintenance Tips:
- Brake Fluid:
- Replace every 2-3 years or as recommended by Toyota.
- Check for leaks and fluid level periodically.
- Brake Pads and Rotors:
- Inspect regularly for wear and replace if below the minimum thickness.
- ABS Functionality:
- Monitor the ABS warning light; it indicates system issues that require diagnostics.
- Brake Noise or Vibration:
- Grinding sounds or vibrations during braking could indicate worn pads or warped rotors.
- Parking Brake:
- Ensure proper adjustment and functionality, especially in electronic systems.