P3000 Prius
The diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P3000 for a Toyota Prius is related to the hybrid control system, specifically signaling an issue with the Hybrid Battery Control System.
Alright — let’s get into it! 🚗⚡
❗ P3000 Code on a Toyota Prius — What It Means
- P3000 = Battery Control System Malfunction
- It’s a hybrid-specific code for Prius models (mostly Gen 1, 2, 3).
- It usually points to issues in the hybrid battery system or the battery control ECU (Electronic Control Unit).
📍 Where the Issue is Located
- Hybrid Battery Pack:
➔ Located behind the back seat, under the trunk area. - Battery Control ECU (Electronic Control Unit):
➔ Attached to or very close to the hybrid battery pack itself. - Wiring and Connectors:
➔ Cables and plug connectors that link the battery to the ECU can also trigger this code if they’re corroded, loose, or damaged.
🔥 Common Causes of P3000
- Aging or failing hybrid battery modules (one or more cells).
- Faulty Battery ECU.
- High-voltage wiring issues (like corrosion or broken connections).
- Cooling fan for the hybrid battery is clogged or malfunctioning (overheating the battery).
🛠️ Quick Diagnostic Steps
- Scan for sub-codes (like P0A80, P3011–P3024) — they will point to specific weak cells in the battery.
- Inspect the battery fan for dust buildup.
- Check battery voltages across modules — you want each one around 7.2–7.8V when healthy.
- Look for water leaks in the trunk — water can damage the battery or ECU.
⚡ Important:
Driving with a P3000 code can cause your Prius to enter “limp mode” (reduced power) or eventually fail to start, so it’s smart to fix it soon.
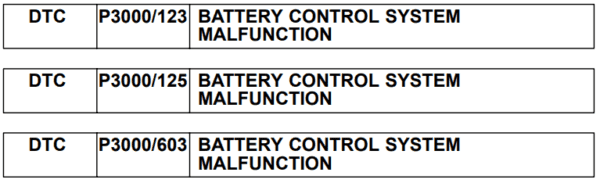
Code Definition
- Code: P3000
- Description: “Battery Control System Malfunction”
This code is a general indicator of a problem within the hybrid battery system or its management, often requiring additional subcodes (INF codes) to pinpoint the exact issue.
Common Causes of P3000
- Hybrid Battery Malfunction:
- Degraded or failing battery modules in the hybrid battery pack.
- Battery Management System (BMS) Issues:
- Malfunction in the battery ECU (Electronic Control Unit) that monitors and controls the hybrid battery.
- Battery Cooling System Problems:
- A clogged or malfunctioning cooling fan can lead to overheating of the hybrid battery.
- Electrical Connection Issues:
- Corroded or loose connections within the hybrid battery system.
- Subcode-Specific Problems:
- The exact cause may vary depending on the INF (sub) codes associated with P3000.
Symptoms of P3000
- Check Engine Light (CEL): Illuminated MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp).
- Warning Messages: Hybrid system or battery warnings on the dashboard.
- Reduced Performance: The vehicle may rely more on the gas engine, resulting in poor fuel economy.
- Limited Power or Limp Mode: In severe cases, the vehicle restricts power to protect the system.
- Overheating: Elevated temperatures in the battery pack if the cooling system is compromised.
Subcodes (INF Codes)
The P3000 code often comes with additional subcodes (INF codes) that provide more detail about the issue. Examples include:
- INF 123: Problem with the HV battery cooling system.
- INF 388: Abnormal battery voltage detected.
- INF 389: HV battery overheating.
Use a hybrid-compatible OBD-II scanner to retrieve these subcodes for more accurate diagnostics.
Diagnostic Steps
- Retrieve Codes and Subcodes:
- Use a hybrid-compatible OBD-II scanner to confirm P3000 and check for related codes (e.g., P0A80, P0AFA).
- Inspect Battery Cooling System:
- Check the cooling fan, intake vent, and ducts for blockages or malfunctions.
- Check Battery Module Voltages:
- Use diagnostic software to monitor individual module voltages and identify imbalances.
- Inspect Electrical Connections:
- Examine the wiring harness, connectors, and bus bars for corrosion or damage.
- Test the Battery ECU:
- Ensure the ECU is functioning correctly and communicating with other systems.
Common Fixes
- Replace the Hybrid Battery Pack:
- Replace the entire pack if multiple modules are failing or the degradation is severe.
- Recondition the Battery Pack:
- Replace failing modules and balance the pack (temporary solution).
- Clean or Repair the Cooling System:
- Fix or replace the cooling fan, and clean intake vents and ducts.
- Repair or Replace Electrical Connections:
- Address corrosion or damage in wiring, connectors, or bus bars.
- Replace the Battery ECU:
- If the ECU is faulty, replace it with a new or remanufactured unit.
Estimated Repair Costs
- Hybrid Battery Replacement (New OEM): $2,000–$4,000
- Hybrid Battery Replacement (Refurbished): $1,000–$2,500
- Battery Reconditioning (Module Replacement): $500–$1,500
- Cooling System Repairs: $100–$500
- Battery ECU Replacement: $500–$1,000
Preventive Tips
- Regularly Inspect the Cooling System:
- Keep the intake vent and fan clean and free of obstructions.
- Monitor Battery Health:
- Use diagnostic tools periodically to assess the condition of the hybrid battery.
- Drive Regularly:
- Consistent use helps maintain the battery’s health and performance.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures:
- Park in shaded or temperature-controlled areas when possible.