P1550 Toyota – Battery Current Sensor Circuit
Sure! Here’s a comprehensive explanation of P1550 Toyota Trouble Code related to the Battery Current Sensor, written in more than 600 words with an official resource link at the end.
P1550 Toyota Code – Battery Current Sensor Circuit Malfunction
Overview
On modern Toyota vehicles, DTC P1550 can also indicate a malfunction in the battery current sensor circuit, particularly on newer models such as the Corolla, Camry, RAV4, Highlander, and Prius. This sensor plays a crucial role in monitoring battery charging and discharging behavior, which is vital for maintaining vehicle electrical stability and optimizing fuel efficiency—especially on hybrid models and vehicles with start-stop systems.
Definition
P1550 Toyota – Battery Current Sensor Circuit Malfunction
This code is triggered when the Engine Control Module (ECM) detects abnormal voltage or current signals from the battery current sensor circuit.
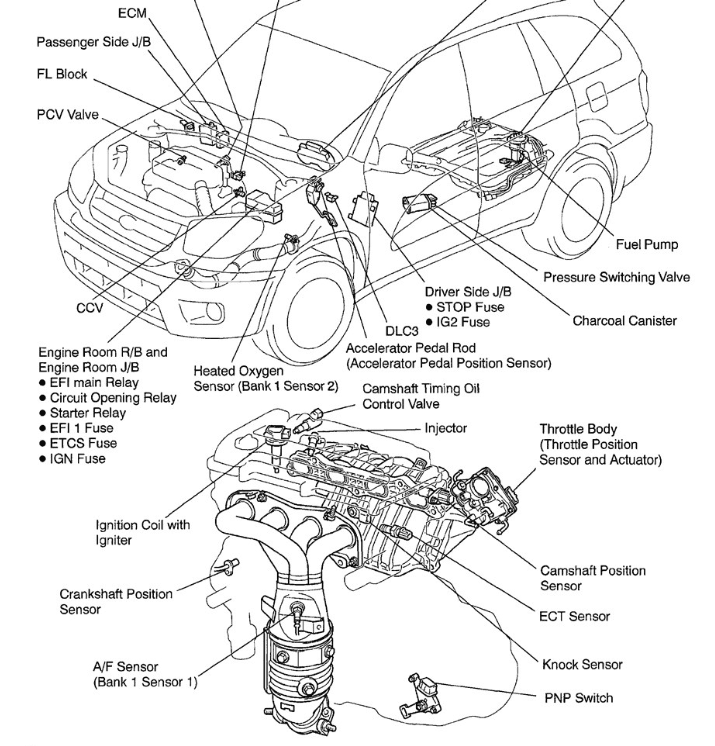
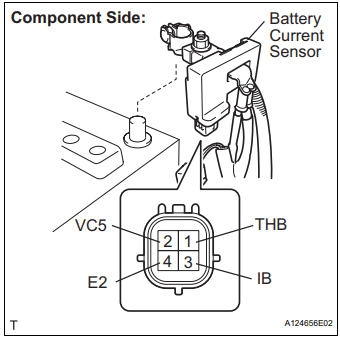
What Is the Battery Current Sensor?
The battery current sensor is typically located on the negative battery terminal or the negative battery cable. It monitors the flow of electrical current into and out of the battery and sends this data to the ECM (Engine Control Module) or BCM (Body Control Module). The ECM uses this data to:
- Control charging system output
- Manage idle stop-start systems
- Optimize battery charging
- Monitor for parasitic drain
- Help with state-of-charge calculations
If the sensor fails or provides erratic data, it can lead to several issues including erratic charging, poor fuel economy, and battery drain.
Symptoms of P1550 (Battery Current Sensor Related)
When P1550 is triggered due to a current sensor issue, you may experience:
- Check Engine Light (CEL) or Charging System Warning
- Dimming lights
- Weak starts or longer cranking times
- Start-stop system disabled (on equipped models)
- Inaccurate battery charge readings
- Malfunction of hybrid charging systems
These symptoms may vary depending on whether the vehicle is hybrid, gas-powered, or features idle-stop technology.
Common Causes of Code P1550 Toyota (Battery Current Sensor Focused)
- Faulty Battery Current Sensor
- The most likely cause. Sensors can degrade over time or fail outright.
- Loose or Corroded Battery Terminals
- Especially on the negative terminal where the sensor is mounted.
- Damaged or Frayed Sensor Wiring
- Rodents, wear-and-tear, or moisture can affect signal transmission.
- ECM or Charging System Fault
- If the ECM misinterprets sensor data or if the alternator over/undercharges.
- Aftermarket Battery or Poor Installation
- Some aftermarket setups may not properly integrate with Toyota’s current sensing systems.
Diagnosis and Troubleshooting Steps
Step 1: Confirm the Code
- Use an OBD-II scanner to verify P1550 and check for any related codes (like P0AFA, U0121, etc.).
- Record freeze-frame data to understand when the issue occurred (engine load, voltage, etc.).
Step 2: Inspect the Battery Terminal Area
- Locate the current sensor (usually on the negative cable).
- Look for corrosion, rust, loose clamps, or signs of overheating.
- Clean and tighten the terminals if needed.
Step 3: Visual Check of Wiring
- Follow the wiring harness from the sensor to the ECM.
- Look for any broken wires, worn insulation, or disconnected plugs.
Step 4: Check Sensor with a Multimeter
- Most current sensors will have three wires: a power, ground, and signal wire.
- Test for proper reference voltage and continuity.
- Compare resistance or voltage readings against Toyota specs.
Step 5: Check Alternator and Charging System
- Ensure the alternator is providing consistent voltage (around 13.5V–14.7V at idle with accessories on).
- A failing alternator can trigger this code indirectly.
How to Fix Code P1550 (Battery Sensor Variant)
1. Replace the Battery Current Sensor
- Cost: $100–$250 (OEM part)
- Labor: Typically 30 minutes to 1 hour.
- Make sure to clear the code after installation and perform a battery sensor calibration if needed.
2. Clean and Reconnect Battery Terminals
- Especially if you see greenish or white corrosion around the clamps.
- Apply dielectric grease after cleaning.
3. Repair or Replace Damaged Wiring
- Replace broken or corroded sensor harnesses.
- Re-pin connectors if terminals are loose or rusted.
4. Reprogram ECM (rare)
- In rare cases, a software update may be necessary to reset the sensor parameters.
Estimated Repair Cost Breakdown
| Repair Task | Estimated Cost (Parts & Labor) |
|---|---|
| Battery Current Sensor Replacement | $150 – $300 |
| Terminal Cleaning and Reconnection | $20 – $50 |
| Wiring Harness Repair | $75 – $150 |
| ECM Flashing (if required) | $100 – $200 |
Can I Still Drive With P1550?
Technically, yes—but with caution. The car may run fine for a while, but improper charging behavior can:
- Damage the battery
- Cause no-starts
- Disable fuel-saving features like idle-stop
- Trigger more faults over time
Fixing it early prevents these headaches and ensures the health of your battery and electrical system.
Helpful Resource
To access official Toyota wiring diagrams, sensor specs, and repair instructions, visit the Toyota technical information site:
🔧 Toyota Tech Info – techinfo.toyota.com
(Subscription may be required for in-depth service manuals.)
Conclusion
DTC P1550 on Toyota vehicles can indicate a Battery Current Sensor Circuit Malfunction, especially in newer models with modern energy management systems. Addressing this code early ensures your battery charges properly, your vehicle’s idle-stop system works efficiently, and your alternator isn’t overstressed. In most cases, a simple sensor replacement or terminal cleaning can fix the issue—saving you time and costly battery problems down the line.
If you need a walkthrough for your specific Toyota model, let me know the year and trim, and I’ll tailor a step-by-step guide for you!