2014 Toyota Corolla won’t start but cranks
If your 2014 Toyota Corolla cranks but won’t start, the issue typically lies with one of the key systems: fuel delivery, ignition, or engine management. Here’s a systematic guide to diagnose and fix the problem:
Possible Causes and Solutions
1. Fuel System Issues
Symptoms:
- The engine cranks but doesn’t catch or start.
- No smell of fuel from the exhaust after cranking.
Diagnosis:
- Check Fuel Level:
- Ensure the fuel tank isn’t empty.
- Listen for the Fuel Pump:
- Turn the key to the “ON” position without cranking.
- Listen for a humming sound from the fuel pump near the rear of the car.
Solutions:
- Fuel Pump Failure:
- If you don’t hear the pump, it may have failed. Test the pump using a multimeter or replace it.
- Clogged Fuel Filter:
- Replace the filter if it’s obstructed.
- Fuel Injectors:
- Inspect injectors for blockages or electrical faults.
2. Ignition System Issues
Symptoms:
- Engine cranks, but there’s no spark at the spark plugs.
Diagnosis:
- Inspect Spark Plugs:
- Remove one plug and inspect it for wear or fouling.
- Test for Spark:
- Attach a spark tester to the plug wire and crank the engine. Look for a bright blue spark.
Solutions:
- Worn Spark Plugs:
- Replace if they are fouled or worn.
- Faulty Ignition Coils:
- Test each coil using an ohmmeter or a diagnostic tool. Replace any that are defective.
- Crankshaft Position Sensor:
- If there’s no spark at all, test the crankshaft position sensor. Replace it if faulty.
3. Engine Management Issues
Symptoms:
- Check Engine Light may be on.
- No other mechanical issues are apparent.
Diagnosis:
- Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs):
- Use an OBD-II scanner to check for error codes.
- Inspect Sensors:
- Common culprits include the Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF) and Camshaft Position Sensor.
Solutions:
- Faulty Sensors:
- Clean or replace the MAF sensor.
- Replace the camshaft position sensor if DTCs indicate a failure.
- ECU Issues:
- Reset the ECU by disconnecting the battery for 10 minutes. If the problem persists, the ECU may require reprogramming or replacement.
4. Air Supply Issues
Symptoms:
- Engine cranks but stalls immediately or doesn’t start at all.
Diagnosis:
- Check the Air Filter:
- Inspect the filter for dirt or blockages.
- Inspect the Throttle Body:
- Look for carbon buildup that may restrict airflow.
Solutions:
- Dirty Air Filter:
- Replace the air filter if clogged.
- Throttle Body Cleaning:
- Clean the throttle body using throttle body cleaner.
5. Timing or Compression Issues
Symptoms:
- The engine cranks unevenly or with a strange sound.
Diagnosis:
- Check Timing Belt/Chain:
- Listen for unusual noises indicating timing problems.
- Perform a Compression Test:
- Use a compression gauge to test the cylinders.
Solutions:
- Timing Chain Issues:
- Inspect and replace the chain or tensioner if necessary.
- Low Compression:
- Address internal engine issues like worn piston rings or a blown head gasket.
6. Immobilizer or Key Issues
Symptoms:
- The security light stays on or flashes on the dashboard.
Diagnosis:
- Test the Key:
- Try starting the car with a spare key.
- Check the Immobilizer System:
- Ensure the key is programmed to the car.
Solutions:
- Reprogram the Key:
- Visit a dealership or locksmith to reprogram the key.
- Reset the Immobilizer:
- Disconnect the battery for 10 minutes to reset the system.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Checklist
- Ensure Fuel is Reaching the Engine:
- Check the fuel pump, filter, and injectors.
- Test for Spark:
- Inspect plugs and coils; test the crankshaft sensor.
- Scan for Codes:
- Use an OBD-II scanner to find potential faults.
- Verify Airflow:
- Check the air filter and clean the throttle body.
- Check for Immobilizer Issues:
- Look for security system faults.
Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide to address all potential causes of a 2014 Toyota Corolla cranking but not starting. Follow these instructions systematically to identify and fix the problem.
1. Ensure Fuel Delivery to the Engine
Check Fuel Pump
- Turn the key to the “ON” position without cranking the engine.
- Listen near the fuel tank for a humming sound.
- No Sound: Likely a fuel pump issue.
- Sound Present: Move to the next step.
Test Fuel Pressure
- Use a fuel pressure gauge. Attach it to the Schrader valve on the fuel rail.
- A healthy pressure for a 2014 Corolla should be 35–50 psi.
- If pressure is low or absent, check the fuel pump, relay, and filter.
Replace Fuel Filter
- Replace the filter if it’s clogged or overdue for maintenance.
Clean Fuel Injectors
- Disconnect the fuel injector wiring harness.
- Use a fuel injector cleaning kit.
- Reconnect the harness and test.
2. Test the Ignition System
Inspect Spark Plugs
- Remove a spark plug and inspect for fouling or wear.
- Replace if:
- The electrode is worn.
- There’s excessive carbon buildup.
Test for Spark
- Attach a spark tester to the plug wire and crank the engine.
- Look for a strong blue spark.
- No Spark: Move to ignition coils and sensors.
Check Ignition Coils
- Remove each coil and test with a multimeter.
- Replace any coil that shows improper resistance.
Inspect Crankshaft Position Sensor
- Locate the sensor near the crankshaft pulley.
- Test the sensor with a multimeter or scan for related fault codes (e.g., P0335).
- Replace if faulty.
3. Scan and Address Engine Management Issues
OBD-II Scan
- Connect an OBD-II scanner to the port under the dashboard.
- Record any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and address them:
- Example: P0101 (Mass Airflow Sensor), P0340 (Camshaft Sensor).
Clean the Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF)
- Disconnect the sensor wiring harness.
- Spray MAF cleaner on the sensor.
- Reinstall and test.
Inspect and Replace Camshaft Position Sensor
- Test the sensor with a multimeter.
- Replace if faulty or if related DTCs are present.
4. Ensure Adequate Airflow
Inspect the Air Filter
- Remove the air filter and hold it up to light.
- Dirty or Blocked: Replace it.
Clean the Throttle Body
- Disconnect the air intake hose.
- Spray throttle body cleaner on the butterfly valve and wipe with a cloth.
- Reassemble and test.
5. Check Engine Timing and Compression
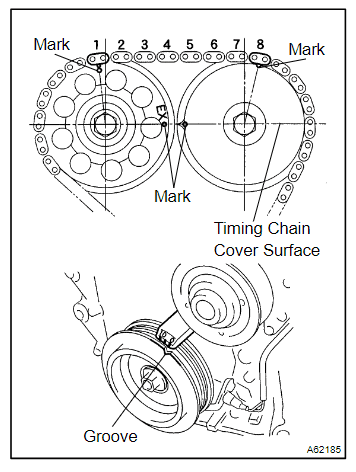
Inspect Timing Chain
- Remove the timing cover and inspect for proper alignment.
- Misaligned timing may require professional adjustment.
Perform a Compression Test
- Remove the spark plugs.
- Insert a compression gauge into each cylinder and crank the engine.
- Healthy Compression: 160–180 psi per cylinder.
- Low compression may indicate internal engine issues (e.g., head gasket failure).
6. Test Relays and Fuses
Locate the Fuse Box
- Check under the hood and dashboard. Refer to the fuse box diagram.
Test Fuses
- Use a fuse tester or multimeter.
- Replace blown fuses with ones of the same rating.
Test Starter Relay
- Swap the starter relay with a similar relay from the fuse box.
- Replace if faulty.
7. Inspect and Repair Ground Connections
- Locate the negative battery terminal and its ground point on the chassis.
- Remove the ground cable and sand both the terminal and chassis connection.
- Reattach securely and test.
8. Address Potential Immobilizer Issues
Check Security Light
- If the security light is flashing, the immobilizer may not recognize the key.
Reprogram the Key
- Try starting with a spare key.
- Visit a Toyota dealership or locksmith to reprogram the immobilizer if needed.
Reset the Immobilizer System
- Disconnect the battery for 10 minutes.
- Reconnect and try starting the car.
9. Diagnose and Replace the Ignition Switch
Test Ignition Switch
- Turn the key and check if accessories (radio, lights) work.
- If intermittent, replace the ignition switch.
Replacement Steps
- Disconnect the battery.
- Remove dashboard trim to access the ignition switch.
- Replace the switch and reconnect.
10. Check and Replace the Starter Motor
Test the Starter Motor
- Listen for a clicking sound when cranking.
- Use a multimeter to test for voltage at the starter.
Replace the Starter
- Disconnect the battery and starter wiring.
- Remove mounting bolts and replace with a new starter.
Final Checklist
- ✅ Ensure fuel pressure is within specification.
- ✅ Verify spark at all plugs.
- ✅ Address any OBD-II codes.
- ✅ Confirm proper airflow and compression.
- ✅ Inspect electrical connections and fuses.