2007 Toyota Tacoma 1GR FE relay diagram
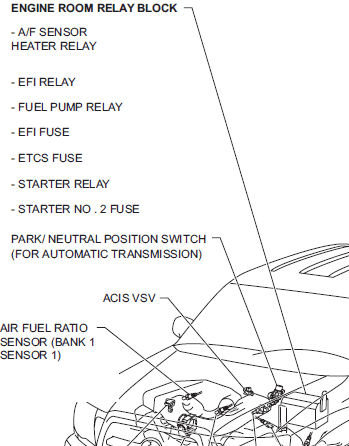
2007 Toyota Tacoma 1GR FE relay diagram – SFI system
The 2007 Toyota Tacoma with the 1GR-FE engine (4.0L V6) relies on multiple relays to manage key systems like the engine, lights, and accessories. Below is a detailed relay diagram and overview of their locations and functions.
Engine Compartment Fuse/Relay Box (1GR-FE)
This is the main relay and fuse box located on the driver’s side of the engine bay near the battery.
| Relay Name | Function |
|---|---|
| EFI Relay | Powers the Engine Control Unit (ECU) and fuel injection system. |
| Starter Relay | Controls the starter motor during ignition. |
| Fan Relays (1 & 2) | Operates the radiator cooling fans. |
| Horn Relay | Activates the horn circuit. |
| Headlight Relay | Powers the low and high beam headlights. |
| AC Magnetic Clutch Relay | Engages the air conditioning compressor. |
| Fog Light Relay | Powers the fog lights (if equipped). |
| ALT-S Relay | Controls the alternator charging system. |
| Fuel Pump Relay | Powers the fuel pump. |
Interior Fuse/Relay Box (Under Driver’s Side Dashboard)
Located under the driver’s side dash near the kick panel.
| Relay Name | Function |
|---|---|
| Power Relay | Powers interior electronics such as the audio system and power outlets. |
| Tail Light Relay | Activates the tail lights. |
| Power Window Relay | Controls the operation of the power windows. |
| Defogger Relay | Powers the rear window defogger. |
| Accessory Relay | Controls auxiliary power when the ignition is in ACC mode. |
Diagram Overview
Engine Bay Diagram
- EFI Relay: Located at the top right corner of the box.
- Starter Relay: Adjacent to the EFI relay.
- Fan Relays: Found near the middle of the box, marked as “Fan No.1” and “Fan No.2.”
- Horn Relay: Positioned near the bottom left corner.
- AC Clutch Relay: Near the fan relays.
Interior Fuse Box Diagram
- Relays are positioned to the left of the fuses. They are typically labeled for easy identification.
Relay Identification Tips
- Labels: The fuse/relay boxes often have a diagram on the cover for quick reference.
- Markings: Each relay is stamped with part numbers or icons indicating its function.
- Testing: Swap a suspect relay with one of the same type from another circuit to verify functionality.
Troubleshooting Common Relay Issues
- Non-Functioning Component:
- Check the associated relay by listening for a click when the circuit is activated.
- Replace if no click is heard or if it fails continuity tests.
- Burnt Relay:
- Inspect for signs of burning or melting, indicating a short circuit or overload.
- Relay Not Getting Power:
- Check the fuse that supplies power to the relay circuit.
Let me know if you need a detailed wiring diagram or specific troubleshooting steps for a relay-controlled system!