2006 Prius Wiring Diagram
The 2006 Toyota Prius electrical wiring system is a sophisticated layout that combines traditional 12V electrical systems with a high-voltage hybrid powertrain. Here’s a breakdown of its main features, key wiring components, and how they interact in the hybrid setup:
🔌 Overview of the 2006 Prius Wiring Diagram
The 2006 Prius uses two major electrical systems:
- 12-volt low-voltage system: Powers traditional electronics like lights, radio, dashboard, ECU, and relays.
- High-voltage (HV) hybrid system: Operates at ~201.6 volts (NiMH battery) and powers the electric motor (MG1 and MG2), inverter/converter, and other hybrid-related components.
🔧 Key Wiring Components and Circuits
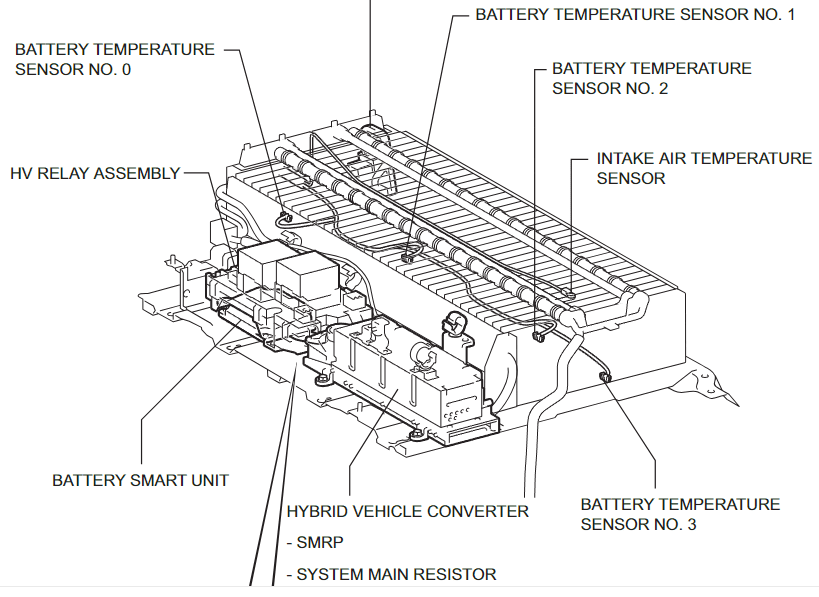
1. Hybrid Battery (Traction Battery) Wiring
- Voltage: ~201.6V DC (28 modules x 7.2V)
- Location: Under the rear seat/trunk area.
- Connects to:
- HV ECU
- Inverter with Converter
- Service plug (for maintenance/safety disconnection)
- Orange-colored high-voltage cables for safety identification.
2. Inverter/Converter Wiring
- Converts HV DC to AC for the motor/generators (MG1 and MG2).
- Also steps down HV to 12V for the auxiliary battery.
- Includes cooling system wiring for inverter pump.
3. Electric Motors MG1/MG2
- MG1 = Starts the engine and acts as a generator.
- MG2 = Drives the wheels.
- Heavy-duty shielded wiring connects these to the inverter.
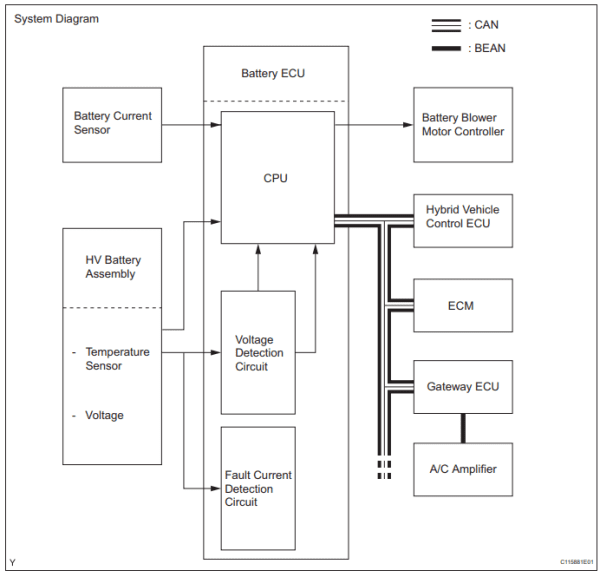
4. ECU and CAN-Bus Communication
- Multiple ECUs: Powertrain Control Module (PCM), Hybrid ECU, Battery ECU, Brake ECU.
- Use CAN-Bus for communication — essential for hybrid operation.
- Wiring includes twisted-pair data cables for signal integrity.
5. Auxiliary 12V Battery Wiring
- Powers:
- ECU wake-up
- Dome lights, radio, accessories
- Ready-state systems
- Connected through main fusible link to junction block.
6. Fuse Boxes and Junction Blocks
- Engine compartment fuse box (high-amperage fuses)
- Instrument panel junction block
- Houses relays, fuses, and integration components like the body ECU.
📘 Where to Find 2006 Prius Wiring Diagram
You can access the full factory wiring diagrams through:
1. Toyota TIS (Technical Information System)
- https://techinfo.toyota.com
- Subscription required (short-term available).
- Offers official electrical wiring diagrams (EWD), connector views, and troubleshooting steps.
2. Third-Party Manuals
- Haynes or Chilton manual for 2004–2009 Prius.
- Includes simplified diagrams.
3. Online Forums and Communities
- PriusChat and Toyota Nation often have shared PDFs or help guides.
- Search for “2006 Prius Electrical Wiring Diagram PDF”.
🛠️ Common Electrical Issues (2006 Prius Wiring Diagram)
- Inverter Coolant Pump Failure
- Symptoms: Warning lights, overheating, loss of power.
- Wiring to the pump and fuse should be checked.
- 12V Battery Low Voltage
- Can cause the car not to start or multiple error lights.
- Wiring to ground connections and battery terminals should be inspected.
- HV Isolation Faults
- Moisture or degradation of HV wires.
- Causes system shutdown or “Check Hybrid System” alert.
- Broken CAN Wiring
- May prevent the car from powering on or cause intermittent faults.
- Look for damaged wiring in door harnesses or behind the dashboard.
⚠️ Safety Notes When Handling Wiring – 2006 Prius Wiring Diagram
- Always disconnect the 12V battery and remove the service plug before working on the hybrid system.
- Wear Class 0 high-voltage gloves when dealing with HV cables.
- Use insulated tools and follow all safety protocols.
- Never probe HV orange wires unless you’re certified and trained.
If you want a PDF wiring diagram, a specific circuit diagram (e.g., headlights, inverter, CAN network), or tips on how to troubleshoot a certain issue, just let me know and I can help generate or locate it for you.
2006 Prius Wiring Diagram PDF
2006 Prius Specs
Background and Significance
Introduced in late 2003 as a 2004 model, the second‑generation Toyota Prius (often called the “NHW20”) debuted for the 2006 model year in North America. Building on the pioneering first‑generation Prius (1997–2003), the 2006 Prius cemented Toyota’s leadership in hybrid technology by improving performance, refinement, cargo space, and safety. It became the world’s best‑selling hybrid at the time, symbolizing the shift toward fuel‑efficient, environmentally conscious transportation in the mid‑2000s.
Hybrid Powertrain and Mechanics
At the heart of the 2006 Prius is Toyota’s second‑generation Hybrid Synergy Drive (HSD) system:
- Gasoline Engine: A 1.5‑liter, 4‑cylinder Atkinson‑cycle engine producing 76 horsepower. The Atkinson cycle sacrifices some peak power in exchange for higher thermal efficiency, optimizing fuel consumption.
- Electric Motor: A 67‑hp permanent‑magnet electric motor delivers instant torque for city driving and aids the gasoline engine under load.
- Combined Output: Although the sum of individual ratings exceeds 143 hp, Toyota rates combined output at 110 hp due to overlaps in powerbands.
- Battery Pack: A 201.6‑volt nickel‑metal hydride (NiMH) battery pack is mounted beneath the cargo area. It’s robust, proven technology, though heavier and larger than today’s lithium‑ion alternatives.
- Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT): The electronic CVT seamlessly blends engine and motor power, smoothing acceleration and maximizing efficiency.
This setup allows electric‑only operation (at low speeds), gasoline‑only, or any combination. Regenerative braking recovers energy during deceleration, recharging the battery. Toyota’s engineering balances a refined driving experience with class‑leading fuel economy.
Performance and Driving Characteristics
- Acceleration: 0–60 mph in roughly 10.5 seconds—adequate for daily driving but modest compared to conventional compact cars of the era.
- Handling: The Prius’s weight distribution (battery toward the rear) and low center of gravity afford surprisingly neutral handling. Body roll is controlled, though the soft suspension prioritizes comfort over sportiness.
- Ride Quality: Tuned for comfort, the 2006 model soaks up bumps well. Road noise is moderate; wind noise at highway speeds is perceptible but not intrusive.
- Braking: The combination of hydraulic and regenerative brakes requires some acclimation—initial pedal travel can feel soft, then firms up as the hydraulic system engages.
Drivers praising the Prius often highlight its smooth transitions between power sources and its serenity at low speeds when running in electric‑only mode.
Interior, Comfort, and Cargo
- Seating and Space: Seating for five in a tall‑roof hatchback body allows good headroom front and rear. The rear bench is reasonably comfortable for adults on short trips, though legroom is tighter than rival compact sedans.
- Dashboard Layout: A futuristic, centrally mounted digital gauge cluster displays speed, fuel level, battery charge, and instantaneous MPG. Some drivers find the high‑center display unconventional but easy to read at a glance.
- Materials: Toyota opted for hard‑feeling plastics in many areas to keep cost and weight down; fit and finish remain good, but materials lack the plushness of some competitors.
- Cargo Capacity: With rear seats up, you get about 22.6 cubic feet of space—competitive for the class. Folding the 60/40 split rear seats expands capacity to roughly 44 cu ft, making the Prius one of the most versatile small‑car cargos of its day.
Available options included a power moonroof, automatic climate control (an early electrostatic touch‑screen system), JBL sound system, and navigation—features that added premium appeal.
Fuel Economy and Environmental Impact
The 2006 Prius achieved EPA ratings of 48 mpg city / 45 mpg highway / 46 mpg combined, numbers unprecedented in a non‑diesel passenger car at the time. Real‑world owners often reported mid‑40s on mixed driving and low‑50s in hypermiling conditions. These savings translated into lower operating costs and a smaller carbon footprint—key selling points as consumer awareness of climate change increased.
Safety and Reliability
- Safety Equipment: Standard anti‑lock brakes (ABS), electronic brake‑force distribution (EBD), traction control, stability control (on later 2006 production), front‑seat side‑impact airbags, and full‑length side curtain airbags.
- Crash Ratings: Earned four‑star frontal and five‑star side crash ratings from the U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA).
- Reliability: The second‑generation Prius built on Toyota’s reputation for reliability. Common long‑term concerns include hybrid battery aging (NiMH packs may need replacement around 150–200 k miles) and inverter water‑pump failure. Overall, maintenance costs remain lower than many luxury hybrids.
Market Reception and Legacy
By 2006, the Prius had become the definitive hybrid icon. Its blend of practicality, efficiency, and pioneering technology garnered praise from environmentalists, tech enthusiasts, and mainstream buyers alike. Sales in the U.S. climbed from just over 20,000 units in 2004 to more than 100,000 by 2006, cementing Toyota’s hybrid leadership.
The 2006 Prius’s influence extended beyond sales figures:
- Industry Catalyst: Competitors scrambled to develop their own hybrids or high‑efficiency models.
- Public Awareness: Hybrid ownership became synonymous with environmental responsibility and fuel savings.
- Technology Platform: The HSD system underpinned subsequent Toyota and Lexus hybrids, spanning SUVs (Highlander Hybrid), luxury sedans (Lexus RX 400h), and plug‑in variants (Prius Plug‑In).
Conclusion
The 2006 Toyota Prius stands as a landmark vehicle that mainstreamed hybrid technology. While it never aimed to thrill the enthusiast with lightning acceleration or sporty handling, it redefined expectations of fuel economy, emissions, and everyday practicality. Its well‑balanced powertrain, thoughtful packaging, and proven reliability created a blueprint that Toyota would refine in later generations—and that the entire automotive world would follow. As a used‑car purchase today, a well‑maintained 2006 Prius can still deliver decades of dependable, efficient service to those seeking one of the earliest—and most successful—hybrids on the road.